Tutorial
This tutorial is divided into two sections: Background and Yvis. The Background section briefly describes some important concepts to understand the analysis offered by the Yvis platform. The Yvis section describes how to use the Yvis features and how to interpret the obtained results.
1. Background
1.1. Antibodies
Antibodies or immunoglobulins are vertebrate immune system proteins produced by B cells and capable of binding to antigens with high specificity and affinity. Most antibodies present a Y-shaped portion, formed by two identical pairs of chains. Each chain pair contains one heavy and one light chain, and each chain has a variable domain and one or more constant domains. The variable domain is the antibody portion that interacts with the antigen. All antibody chains have a variable domain formed by two β-sheets, connected face-to-face by a disulphide bond, as shown in Figure 1. Each strand that forms the β-sheets is identified by a letter. The front sheet contains the GFCC’C” strands, and the back sheet contains the ABED strands. Strands are linked by loops among which three are usually involved in antigen binding. These loops are known as Complementarity Determining Regions (CDRs).
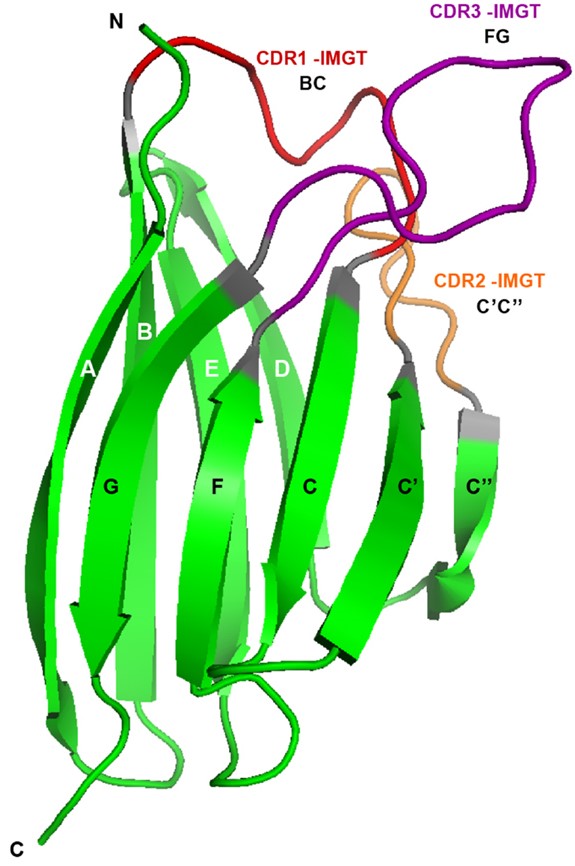
Figure 1: Cartoon representation of the variable domain structure of an antibody chain. Individual letters identify the strands (in green), and the different colours of these letters distinguish the two sheets. The three CDR loops are highlighted in red, orange and purple. Figure from Lefranc M-P (2014).
1.2. Antibody numbering
To compare the variable domain of antibody chains, some numbering schemas were proposed. They were defined based on the superimposition of antibody structures showing that there is a high similarity between some parts of the variable domain of antibody chains, known as frameworks (FWs). The numbering schemas allow the identification of FWs and of the hypervariable regions that are usually associated with the antigen binding and are known as CDRs. When a numbering schema is applied to a sequence, some key residues, which are conserved in the numbering definition, are searched, and gaps are inserted to generate a numbered sequence. Antibody numbering is important in antibody analysis because it provides an implicit sequence alignment between any possible variable domain sequence of an antibody chain, thus delimiting the FWs and CDRs.
1.3. Antibody data visualization
Data visualization allows data representation in a way that can make easier to understand the data significance. The IMGT/Collier de Perles is a visualization tool that represents the amino acid composition of the variable domain of an antibody chain associated with the conserved 3D structure of antibodies. It displays the variable domain sequence in one or two layers (see Figure 2). As the variable domain of all antibody chains has the same structure formed by two β-sheets connected face-to-face, the Collier de Perles on two layers presents the amino acid sequence closer to its 3D structure, by “superimposing” the strands. The Collier de Perles on one layer shows the same data, but in a way that it is closer to the amino acid sequence, by maintaining the sheets in the same order they have in the sequence, not in the structure. Independently of the display option, the Collier de Perles visualization allows visualizing the three CDRs of the variable domain delimited by the positions highlighted by squares. Hatched positions represent gaps in the alignment caused by the IMGT numbering.
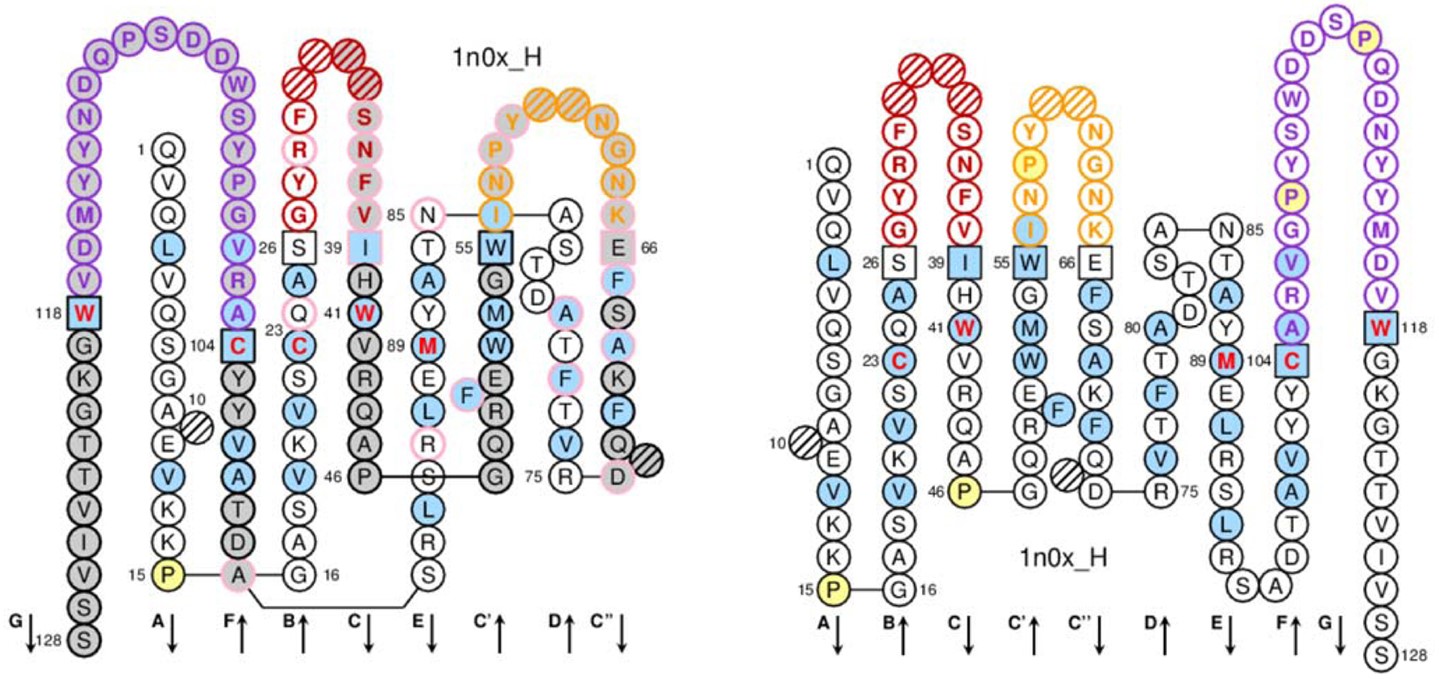
Figure 2: Collier de Perles visualization in two layers (left image) and one layer (right image). Individual letters and arrows identify the strands. The CDR loops are highlighted in red, orange and purple. Figure from Lefranc M-P (2014).
The IMGT/Collier des Perles is a great visualization of the variable domain of an antibody chain, but can only represent one chain per visualization. When it is necessary to analyse multiple antibody chains, normally, researches use classical multiple sequence alignment (MSA) representations. In a classical MSA representation, the rows represent a list of gapped sequences and each column represents an amino acid or gap in a specific position. The colours in a position represent an amino acid group or class, and allow the identification of conserved or variable positions in the alignment, as well as the comparison of positions. The main limitation of this visualization is the limited number of rows and columns that can be shown at one time.
1.4. Collier des Diamants
In Yvis, we offer a new visualization that includes the advantages of the IMGT/Collier de Perles and MSA visualization methods (i.e., representation of antibody sequence closer to the structure to highlight the CDR and FW relations), and the possibility to analyse multiple sequences in the same visualization. This new visualization is based on the IMGT/Collier de Perles (Pearl Necklace) representation. Instead of representing only one amino acid per position, the Collier de Diamants represents multiple amino acids in each position, from a multiple sequence alignment. As each pearl of the necklace is replaced by a new representation with multiple “facets”, this new visualization was called Collier de Diamants (Diamond Necklace).
2. Yvis
The Yvis platform integrates a database of antibody structures data and a set of analysis resources (including the new visualization Collier des Diamants ) that can be used with user sequences or sequences from the Yvis database.
2.1. Yvis database
The Yvis database is an updated collection of data on Protein Data Bank (PDB) structures that contain at least one antibody chain or variable domain fragment. The “Statistics” tab presents the details of the data stored in the Yvis database.
2.2. Input options
Users can analyse their own sequences or sequence data stored in the Yvis database.
If the data source is the Yvis database, users can select among the following search criteria and filter options:
Select this option to show information on all antibody sequences from PDB and stored in Yvis database.
Filter options:
Select "Show engineered antibodies" if you want to show, in the results, sequences marked as engineered in the PDB structure file.
Select "Show only sequences with the right amino acid in conserved positions” to restrict the results to sequences that have the correct amino acid residues in the conserved positions of the IMGT numbering: Cysteine 23, Tryptophan 41, Cysteine 104, Leucine 89 and Phenylalanine or Tryptophan 118.
Select "Show only one VH/VL pair for each PDB file" if you want to show, in the results, only the first pair of light and heavy chains of a PDB structure file. Otherwise, all antibody chains of the structures will be shown.
Select "Use identity filter" and set an identity cut-off if you want to analyse only a set of sequences having at most that identity value.
Select this option to show only chains from structures of a user-defined list of PDB identifiers, with or without chain specification.
You can specify a list of PDB IDs by selecting the "Specify PDB IDs" option and inserting in the textbox the PDB IDs separated by commas, semicolons, or by putting each ID in a new line. In this case, Yvis will show the chains stored in the Yvis database that are part of the indicated structures.
If you want to restrict the analysis to specific chains, you should select the "Specify PDB IDs and chain name" option and insert in the textbox a list of chains separated by commas, semicolons, or in new lines. Each chain must be specified by the PDB ID followed by a colon and the chain name.
Filter options:
Select "Show engineered antibodies" if you want to show, in the results, sequences marked as engineered in the PDB structure file.
Select "Show only sequences with the right amino acid in conserved positions” to restrict the results to sequences that have the correct amino acid residues in the conserved positions of the IMGT numbering: Cysteine 23, Tryptophan 41, Cysteine 104, Leucine 89 and Phenylalanine or Tryptophan 118.
Select "Show only one VH/VL pair for each PDB file" if you want to show, in the results, only the first pair of light and heavy chains of a PDB structure file. Otherwise, all antibody chains of the structures will be shown.
Select "Use identity filter" and set an identity cut-off if you want to analyse only a set of sequences having at most that identity value.
Select this option to show only chains of antibodies produced by specific organisms. Choose one or more species from the list of all antibody-producing organisms stored in the database, standardized by species, based on the UniProt Taxonomy Database.
Filter options:
Select "Show engineered antibodies" if you want to show, in the results, sequences marked as engineered in the PDB structure file.
Select "Show only sequences with the right amino acid in conserved positions” to restrict the results to sequences that have the correct amino acid residues in the conserved positions of the IMGT numbering: Cysteine 23, Tryptophan 41, Cysteine 104, Leucine 89 and Phenylalanine or Tryptophan 118.
Select "Show only one VH/VL pair for each PDB file" if you want to show, in the results, only the first pair of light and heavy chains of a PDB structure file. Otherwise, all antibody chains of the structures will be shown.
Select "Use identity filter" and set an identity cut-off if you want to analyse only a set of sequences having at most that identity value.
Select this option to show only chains from antibody structures that presents an antibody-antigen complex, or choose the "None" option to show only chains of antibodies that are not in complex with antigens. The list presents non-protein antigens type (carbohydrate, hapten, and nucleic acid) and, for proteins or peptide antigens, the antigen-producing organisms stored in the database, standardized by species, based on the UniProt Taxonomy Database. Choose one or more items from this list.
Filter options:
Select "Show engineered antibodies" if you want to show, in the results, sequences marked as engineered in the PDB structure file.
Select "Show only sequences with the right amino acid in conserved positions” to restrict the results to sequences that have the correct amino acid residues in the conserved positions of the IMGT numbering: Cysteine 23, Tryptophan 41, Cysteine 104, Leucine 89 and Phenylalanine or Tryptophan 118.
Select "Show only one VH/VL pair for each PDB file" if you want to show, in the results, only the first pair of light and heavy chains of a PDB structure file. Otherwise, all antibody chains of the structures will be shown.
Select "Use identity filter" and set an identity cut-off if you want to analyse only a set of sequences having at most that identity value.
Select this option to show only chains assigned to specific germline alleles by IMGT/DomainGapAlign. You can restrict the assigned species and V or J alleles by choosing one or more options from the lists. If you do not want to restrict the analysis, select all options.
Filter options:
Select "Show engineered antibodies" if you want to show, in the results, sequences marked as engineered in the PDB structure file.
Select "Show only sequences with the right amino acid in conserved positions” to restrict the results to sequences that have the correct amino acid residues in the conserved positions of the IMGT numbering: Cysteine 23, Tryptophan 41, Cysteine 104, Leucine 89 and Phenylalanine or Tryptophan 118.
Select "Use identity filter" and set an identity cut-off if you want to analyse only a set of sequences having at most that identity value.
Select this option to show only antibody chains from PDB structures filtered on the basis of literature information. You can specify paper title or summary, authors’ names, publication year, or article identifier (DOI, PMID or PMCID). These fields accept multiple keywords and can be defined with Boolean operators (AND, OR and NOT).
Filter options:
Select "Show engineered antibodies" if you want to show, in the results, sequences marked as engineered in the PDB structure file.
Select "Show only sequences with the right amino acid in conserved positions” to restrict the results to sequences that have the correct amino acid residues in the conserved positions of the IMGT numbering: Cysteine 23, Tryptophan 41, Cysteine 104, Leucine 89 and Phenylalanine or Tryptophan 118.
Select "Show only one VH/VL pair for each PDB file" if you want to show, in the results, only the first pair of light and heavy chains of a PDB structure file. Otherwise, all antibody chains of the structures will be shown.
Select "Use identity filter" and set an identity cut-off if you want to analyse only a set of sequences having at most that identity value.
If using own data, the user can choose among the following input options:
Select this option to insert a FASTA file that contains amino acid sequences of variable domains of antibody chains. The Yvis server uses ANARCI to gap sequences.
In sequence name and comments line (line starting with ">"), the user can insert the following information, separated by "|": PDB/identification source, chain identification, chain type (it is overwritten if ANARCI finds a different type), antibody-producing organism, engineered antibody information (engineered or not), antigen-producing organism, antigen molecule description, assigned germline species, V gene, percentage of V gene identity, J gene, and percentage of J gene identity. These are suggested information and could be used in analysis filters; however, only the sequence identification is mandatory (and will be used in the PDB identification field). Optionally, you can select the option “Extract germline information with ANARCI” to obtain germline information from ANARCI instead of getting them from the user’s file.
As the time of execution of this analysis is in function of the number of uploaded/chosen sequences, in the case of large files this time will be long (the user’s browser might present a slow script dialog). In the case of a huge number of sequences, users are invited first to submit them to IMGT/DomainGapAlign and then upload the results page into Yvis, using the “IMGT/DomainGapAligner results file” input option.
Select this option to insert a FASTA file containing complementarity-determining region (CDR) amino acid sequences. Choose the type of CDR sequences (CDR1, CDR2, or CDR3; heavy and light chain are treated in the same way). The sequence length must be at most equal to the number of amino acids indicated in each CDR. The Yvis platform will gap sequences according to the chosen CDR. In sequence name and comments line (line starting with ">"), the user can insert the following information, separated by "|": PDB/identification source, chain identification, chain type (H or L, otherwise the information will be ignored), antibody-producing organism, engineered antibody information (engineered or not), antigen-producing organism, antigen molecule description, assigned germline species, V gene, percentage of V gene identity, J gene, and percentage of J gene identity. These are suggested data and could be used in analysis filters; however, only the sequence identification is mandatory (and will be used in the PDB identification field).
Select this option to insert an IMGT/DomainGapAlign results file. IMGT/DomainGapAlign allows aligning amino acid sequences, gapping uploaded sequences, and indicating the closest germline V and J genes. When uploading sequences into IMGT/DomainGapAlign, it is recommended to choose 1 as input in the "Displayed alignments" option, because all displayed alignment sequences will be analysed by Yvis, even if there are multiple alignments of the same sequence. After submitting sequences to IMGT/DomainGapAlign, save the webpage that presents the results in your computer (HTML file: .htm or .html extension). Then submit this file to Yvis.
Yvis will process the submitted file on the user’s web browser, extracting the chain identification, chain type, and antibody numbering and germline information. As IMGT/DomainGapAlign ignores the additional information passed on the sequence headers from the FASTA file, some information will be missing in the data table (e.g., engineered, antigen and antibody species, and molecule description).
Select this option to insert an IMGT/HighV-QUEST results file. IMGT/HighV-QUEST analyses next-generation sequencing (NGS) data on antigen receptors. Users must submit a FASTA file containing the nucleotide sequences to IMGT/HighV-QUEST. This tool will generate a set of files that can be downloaded as a compressed file. After decompressing the file, submit the gapped amino acid file, identified as “4_IMGT-gapped-AA-sequences.txt” to Yvis. This file has a header row followed by several antibody chain rows. Each row has the following fields, as described in IMGT/V-QUEST Documentation, separated by tabs:
- Sequence number
- Sequence ID
- V-DOMAIN Functionality
- V-GENE and allele
- J-GENE and allele
- D-GENE and allele
- Then AA-sequences of:
- V-D-J-REGION: gapped according to the IMGT numbering, if described
- V-J-REGION: gapped according to the IMGT numbering, if described
- V-REGION: gapped according to the IMGT numbering
- FR1-IMGT: gapped according to the IMGT numbering
- CDR1-IMGT: gapped according to the IMGT numbering
- FR2-IMGT: gapped according to the IMGT numbering
- CDR2-IMGT: gapped according to the IMGT numbering
- FR3-IMGT: gapped according to the IMGT numbering
- CDR3-IMGT
- JUNCTION
- J-REGION
- FR4-IMGT
Yvis will present the Collier de Diamants visualization of sequences that are marked as productive in “V-DOMAIN Functionality” and do not have ambiguous amino acids.
As the time of execution of this analysis is in function of the number of inputted sequences, users should be patient in the case of large files, even if their browser presents a slow script dialog.
Select this option to upload a FASTA file containing gapped amino acid sequences of variable domains of antibodies chains. As Yvis will not change the sequences, they must be aligned in the submitted file. If the uploaded sequences have CDR3 insertions, the user must indicate the number of insertions in the corresponding field. It is also possible to insert a sequence of only one part of the variable domain. In this case, the first and last positions in the corresponding fields must be changed.
In sequence name and comments line (line starting with ">"), the user can insert the following information, separated by "|": PDB/source identification, chain identification, chain type (H or L, otherwise the information will be ignored), antibody-producing organism, engineered antibody information (engineered or not), antigen-producing organism, antigen molecule description, assigned germline species, V gene, percentage of V gene identity, J gene, and percentage of J gene identity. These are suggested information and could be used in analysis filters. However, only the sequence identification is mandatory (and will be used in the PDB identification field).
2.3. Result Analysis
After the user defined the data to be analysed and clicked on the “Analyse” button, Yvis will present a page containing the search criteria or input data at the top, and the filter options on the left. On the right side of the page, Yvis will present the input for the comparison feature and the Collier de Diamants visualization of sequences. On the bottom of the page, Yvis presents a table with information on each analysed sequence. These features are explained below.
2.3.1. Collier de Diamants interpretation
Collier de Diamants uses IMGT/Collier de Perles (Pearl Necklace) representation to present a multiple sequence alignment. Each Collier de Diamants position corresponds to a column in a classic multiple sequence alignment visualization, and it is summarized by a pie chart. In this chart, each “pie slice” (sector) represents the number of sequences with an amino acid of a specific class (defined by a colour) in that position. The amino acid classes and colours are the same as in WebLogo (Crooks et al., 2004) where they are classified according to their chemical properties. Thus, green represents polar amino acids (G, S, T, Y, C, Q, N), blue represents basic (K, R, H), red represents acidic (D, E), and black represents hydrophobic amino acids (A, V, L, I, P, W, F, M). In Yvis, gaps are in grey. The Collier de Diamants presents the most frequent classes in a clockwise orientation.
The Collier de Diamants shows the positions as in Collier de Perles, linking sequences to their 3D structure. Squares indicate the CDR anchors, one position before the CDR start and one after the CDR end (i.e., green for CDR1, orange for CDR2, and blue for CDR3) and allow the quick visualization of the residues that compose each CDR. As the Collier de Diamants uses the IMGT numbering schema to align sequences, CDR1 corresponds to positions 27-38, CDR2 corresponds to positions 56-65, and CDR3 corresponds to position 105-117, regardless of the chain type (heavy or light). CDR3 may contain some insertions when longer than 13 amino acids. In this case, as indicated by the IMGT numbering schema, Yvis insert new position between positions 111 and 112, in the following order: 112.1, 111.1, 112.2, 111.2, 112.3, 111.3, etc.
Like the IMGT/Collier de Perles, Collier de Diamantscan be presented in one or two layers. The two-layers version presents the variable domain strands in a position closer to the 3D structure, while the one-layer version has a representation closer to the variable domain sequence. To change the presentation from one to two layers (or vice versa), click on the switch button on the top of Collier de Diamants representation. The strands of the variable domain are identified by letters (A-G) and arrows at the bottom of Collier de Diamants visualization. Moreover, the arrow colour indicates the different sheets of the variable domain.
The Collier de Diamants representation allows visualizing position(s) with a conserved class of residues and their position in the 3D structure. This can be easily done because positions with a conserved residue class will present a dominant sector in the corresponding pie chart. Conversely, variable positions (based on the multiple sequence alignment) will be represented by pie charts with many different sectors.
To identify the amino acids present in each position, the user can click on each position to open a new chart with the detailed amino acid composition of that position. This is a classical bar chart where each bar represents an amino acid, and its colour corresponds to the amino acid class. The bar height represents the number of sequences that have this amino acid in that position. The user can hover the mouse pointer over the bar to see the exact number of amino acids. Bars can be sorted according to their height or the represented amino acid. By clicking on “Close”, the bar chart is closed, and the Collier de Diamants visualization is back.
Besides the visualization of a multiple sequence alignment, Collier de Diamants can display a quantitative attribute for each position, represented by circles in salmon around each pie chart. In the Yvis platform, this attribute is shown when Yvis database chains from structures of protein antigen-antibody complexes are analysed. It represents the number of chains with a putative contact at that position. Yvis defines a putative contact when the distance between alfa-carbons of an antibody amino acid is shorter than 8Å. The radius of the contact circle (in salmon) around the pie chart of a given position will be proportionally bigger in function of the number of sequences with a putative contact in that position. By hovering the mouse pointer over a position in the pie chart, the user can see, exactly, the number of antibody chains that have a putative contact in that position. The total number of analysed sequences with putative contact information is indicated at the top of the Collier de Diamants visualization, as well as the maximum number of contacts at a position.
Contacts are important information in antibody analysis because the positions making putative contacts are usually related to antibody-antigen binding. The user can show/hide contact information by selecting/unselecting the “Show contact info” box.
The Collier de Diamants visualization can be saved by clicking the “Save image” button. Yvis will generate a PNG or SVG image that can be downloaded.
2.3.2. Comparison tool
The Yvis platform allows also comparing the multiple sequence alignment with another sequence, for instance a target sequence, a germline gene sequence, or a consensus sequence. For this, the aligned or unaligned sequence must be inserted in the box above the Collier de Diamants representation. Then, the user must select the option “Use the sequence as it is” for aligned sequences, or the option “Insert gaps in the sequence, if necessary” for unaligned sequences. In this case, the Yvis server will use ANARCI to align the sequence, inserting gaps when required.
When the user upload a sequence to be compared with the multiple sequence alignment presented in the Collier de Diamants, Yvis will display, at the centre of each pie chart that represents a position, a small circle with the inputted sequence amino acid corresponding to that position. This circle is coloured according to the colour schema used for the pie chart sectors. This allows the easy comparison of the sequence with the multiple sequence alignment, just by comparing the colour of the small circle and that of the largest sector of the pie chart for that position. Thus, with this representation, divergent sequence positions in the multiple sequence alignment are represented by colours that are different from the one of the predominant slice.
2.3.3. Filter options
Generally, the user wishes to analyse a subset of the initial dataset (for example, only heavy chains or only human antibodies against a specific antigen). A set of filters is available after the user’s initial search or input data to generate these specific datasets. These filters are on the right side of Collier de Diamants: chain type (heavy/light), antibody-producing organism, antigen type or producing organism (for protein or peptide antigens), antigen molecule description, and germline information. This last filter is defined by assigned germline species and V or J germline gene. By clicking on each filter type, the user can expand it, and see the options related to the initial set of analysed sequences. The number of sequences that satisfy each filter option is exhibit after it. All these filters can be combined and can be undone just by selecting the corresponding boxes.
2.3.4. Data table
When showing the Collier de Diamants, the Yvis platform will present, below the visualization, a table containing the information available for all chains presented in the multiple sequence alignment. This table contains the data stored in the Yvis database (when chosen as input method), or the header/identification for user files. Independently of the input type, the gapped sequence used in the multiple sequence alignment is also shown. This table can be exported in CSV format to be used with other tools.
This information table contains the following fields: PDB/source identification, chain identification, chain type (heavy or light), antibody-producing organism, engineered antibody information (if the chain was marked as engineered), antigen-producing organism, antigen molecule description, gapped and ungapped chain sequences, assigned germline species, V gene, percentage of V gene identity, J gene, and percentage of J gene identity. At the gapped sequence column, the CDR positions are highlighted (green for CDR1, orange for CDR2, and blue for CDR3) as well as the putative contacts (salmon).